SaaS-to-SaaS Phishing: The Hidden Threat in Your Email Security
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly relying on Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions to drive efficiency and productivity. A recent study by BetterCloud reveals that organizations now use an average of 110 SaaS applications, a number that has skyrocketed in recent years. While this proliferation of SaaS tools offers numerous benefits, it has also significantly expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals.
One particularly alarming trend is the rise of SaaS-to-SaaS phishing attacks. These sophisticated exploits leverage the interconnected nature of SaaS ecosystems to compromise entire networks of applications through a single point of entry. As organizations continue to adopt more SaaS solutions, the need for robust email security has never been more critical.
The SaaS Explosion and Its Security Implications
The adoption of SaaS solutions has been nothing short of revolutionary. Gartner predicts that the global SaaS market will reach $195 billion by 2025, underscoring the growing dependence on cloud-based applications.
Here are some statistics:
- 70% of business applications are now SaaS-based
- The average employee uses 36 cloud services at work
This extensive use of SaaS applications creates a complex web of interconnected services, each potentially serving as an entry point for attackers.
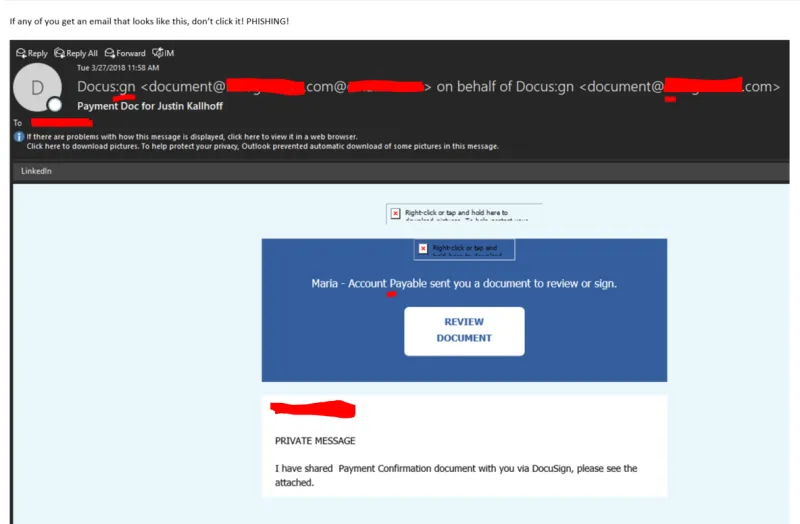
DocuSign Phishing Mail (Credits: Team Ascend)
The Mechanics of SaaS-to-SaaS Phishing
Unlike traditional phishing attacks that typically aim to steal credentials or deploy malware, SaaS-to-SaaS phishing exploits the trust relationships between integrated SaaS platforms. Here's how a typical attack might unfold:
- The attacker sends a phishing email impersonating a legitimate SaaS provider.
- An unsuspecting user clicks on a link and enters their credentials on a fake login page.
- The attacker uses these credentials to access the compromised SaaS account.
- Leveraging OAuth connections and API integrations, the attacker moves laterally to other connected SaaS applications.
- Sensitive data is exfiltrated or further malicious actions are taken across multiple platforms.
The Inadequacy of Traditional Email Security
Many organizations have implemented email security solutions, but these tools are often ill-equipped to handle the nuanced threats posed by SaaS-to-SaaS phishing attacks. The limitations include:
- Limited visibility into SaaS integrations and OAuth permissions
- Inability to detect sophisticated impersonation tactics
- Lack of post-delivery protection
- Insufficient context awareness of SaaS ecosystems in the organisation
- Reliance on static, rule-based systems that can't keep pace with evolving threats
A study byPonemon Institute found that 65% of IT and security professionals believe their current email security solutions are ineffective against advanced email threats, including those targeting SaaS applications.
Real-Life Case Studies of SaaS-to-SaaS Phishing
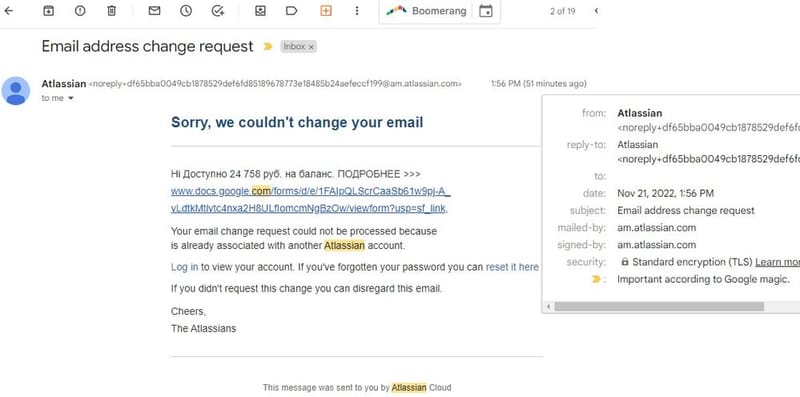
To illustrate the severity of these threats, consider the following recent incidents:
- The Zoom Credential Harvesting Campaign (2020): Attackers exploited the surge in Zoom usage during the pandemic, compromising thousands of corporate user credentials and potentially breaching multiple connected SaaS platforms.
- The Microsoft 365 to Salesforce Attack (2021): Cybercriminals compromised Microsoft 365 accounts and manipulated OAuth permissions to access Salesforce instances, leading to significant data breaches across organizations.
- The DocuSign Supply Chain Attack (2022): Attackers gained access to DocuSign accounts and exploited integrations with tools like Google Workspace and Dropbox, resulting in unauthorized document alterations and data leaks.
- The Slack to GitHub Breach (2023): Threat actors compromised Slack accounts and exploited Slack-GitHub integrations, leading to source code theft and potential injection of malicious code into repositories.
- The HubSpot CRM Exploit (2022): Cybercriminals accessed HubSpot accounts and leveraged integrations with email marketing and customer support platforms, launching further phishing campaigns and accessing sensitive customer communications.
The Impact of SaaS-to-SaaS Phishing
The consequences of these attacks can be severe and far-reaching for organizations. Here are the top five impacts:
- Widespread Data Breaches: A single point of entry can lead to extensive data loss across multiple interconnected SaaS platforms, exposing sensitive information and intellectual property.
- Significant Financial Losses: Organizations face direct costs from theft or fraud, as well as expenses related to incident response, recovery efforts, and potential regulatory fines. Long-term financial impacts can result from reputational damage and customer churn.
- Operational Disruption and Productivity Loss: Critical SaaS applications may face downtime during investigation and recovery, disrupting core business processes and resulting in significant productivity losses.
- Reputational Damage and Loss of Trust: Data breaches and compromised communications can severely damage an organization's reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, negative media coverage, and potential loss of business opportunities.
- Cybersecurity Resource Drain and Long-term Security Implications: Responding to these attacks can overwhelm security teams, necessitate substantial investments in new security measures, and require extensive audits and reconfigurations of SaaS ecosystems.
The Need for Enhanced Email Security
To effectively combat the rising threat of SaaS-to-SaaS phishing, organizations need to adopt more comprehensive email security solutions that:
- Provide deep visibility into SaaS integrations and OAuth permissions
- Employ advanced AI and machine learning to detect subtle signs of impersonation
- Offer continuous post-delivery monitoring and remediation capabilities
- Understand the context of SaaS ecosystems and user behaviors
- Utilize dynamic, adaptive security measures that evolve with emerging threats
Conclusion
As businesses continue to embrace SaaS solutions, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands proportionally. SaaS-to-SaaS phishing represents a significant and growing threat that traditional email security measures are ill-equipped to handle.
One of the primary reasons traditional email security fails to protect against SaaS-to-SaaS phishing attacks is its lack of context-awareness. These conventional solutions often operate in isolation, unable to understand the complex interrelationships between various SaaS applications, user behaviors, and organizational workflows. This lack of contextual understanding leaves organizations vulnerable to sophisticated attacks that exploit the interconnected nature of modern SaaS ecosystems.
To effectively combat these threats, organizations must invest in advanced email security solutions that go beyond simple rule-based filtering. These next-generation solutions should offer:
- Deep context-awareness of the entire SaaS ecosystem
- Real-time analysis of user behaviors and application interactions
- Understanding of normal vs. anomalous patterns in SaaS usage
- Ability to detect subtle signs of impersonation and unauthorized access attempts
- Continuous monitoring and adaptive response capabilities
By adopting such context-aware security measures, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect and prevent SaaS-to-SaaS phishing attacks. This approach allows security systems to understand not just the content of emails, but also the broader context in which they occur, including the relationships between different SaaS applications, user roles, and typical workflow patterns.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to grow in complexity, our approach to securing it must evolve accordingly. Context-aware email security represents a crucial step forward in protecting organizations against the increasingly sophisticated and interconnected threats of the modern digital landscape. By prioritizing this aspect of cybersecurity, businesses can ensure that the benefits of SaaS adoption are not overshadowed by increased security risks, allowing them to leverage the full potential of cloud-based technologies safely and confidently.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted