[Sep 2025 Update] Nifty.com Used as Phishing Infrastructure: How Raven Detected Abuse of Trusted Infrastructure
Editor's Note:This post updates our original May 2025 analysis with new intelligence covering continued threat actor operations through September 2025.
A multi-wave phishing campaign abused legitimate Nifty.com infrastructure to impersonate trusted business workflows and harvest credentials. Raven AI (formerly Ravenmail) detected the attack despite clean headers, valid authentication, and no obvious red flags.
Is Nifty.com Safe?
The short answer: Nifty.com itself is safe — it's a legitimate Japanese internet service provider with millions of users. However, like many free email providers, its infrastructure has been systematically abused by threat actors for sophisticated phishing campaigns.
The real question isn't whether Nifty.com is safe, but whether emails claiming to come from Nifty.com addresses can be trusted. Our research shows that threat actors have weaponized the platform's legitimate authentication to bypass security controls, making it a powerful vector for business email compromise attacks.
This isn't unique to Nifty — similar abuse patterns affect Gmail, Outlook, and other major providers. The difference is in how threat actors have specifically leveraged Nifty's infrastructure combined with other services to create nearly undetectable phishing campaigns targeting high-value business users.

A Campaign Built for Evasion
The attackers didn’t spoof a domain — they used it legitimately.
They registered free accounts on nifty.com, a well-known Japanese ISP, and launched phishing emails directly from its infrastructure. Because these were real accounts, all authentication layers passed:
Protocol | Status |
|---|---|
SPF | ✅ Pass |
DKIM | ✅ Pass |
DMARC | ✅ Aligned |
This alone allowed them to bypass most secure email gateways (SEGs) that rely heavily on these checks.
Campaign Timeline [ Update] : Multiple Waves, Adaptive Behaviour - Persistent Over 8 Months
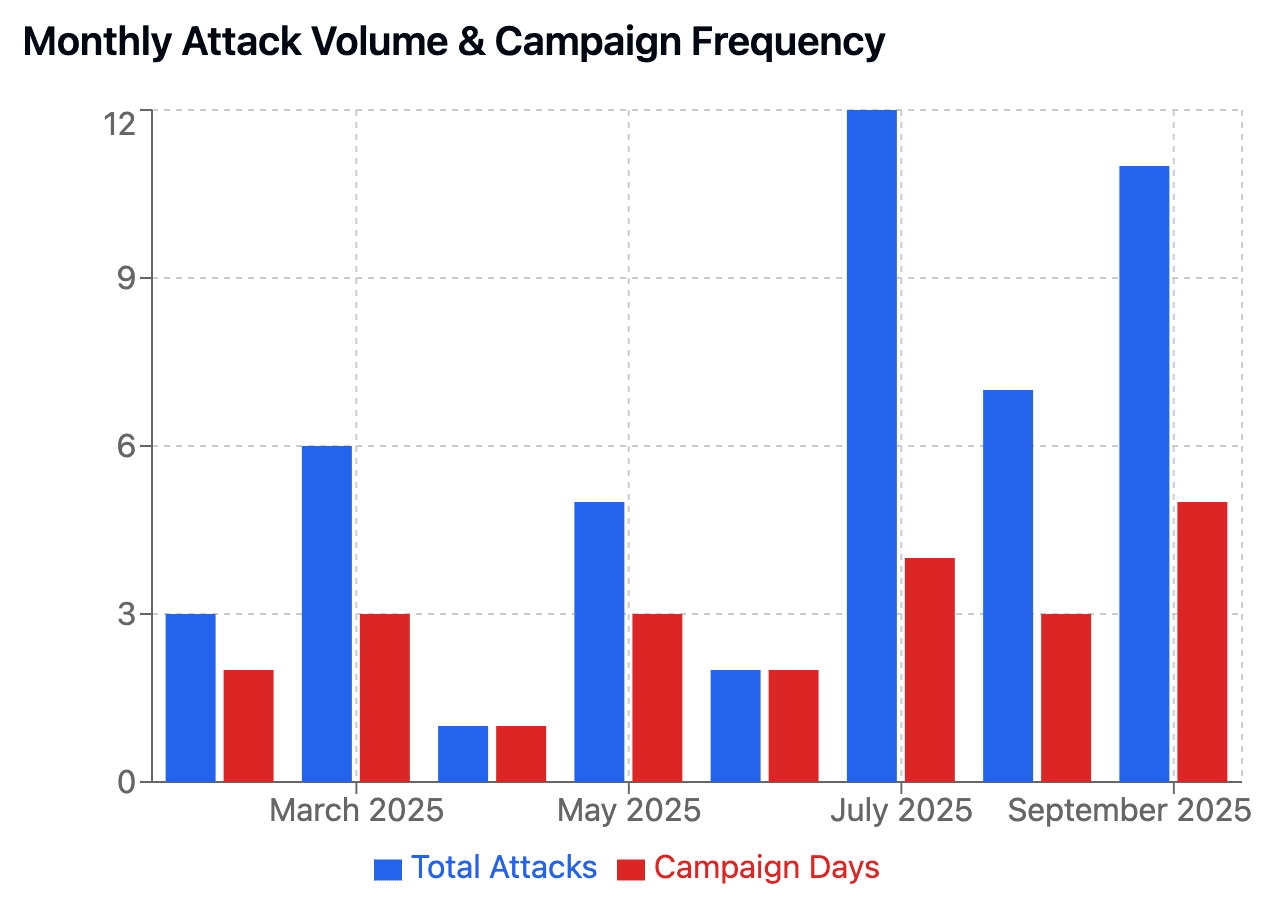
The threat actor has been active for the past 8 months and the number of campaign days have been steadily increasing. The overall sophistication of the attack has increased given the use of new phish kits and multi-target personalization.
Phase | Period | Activity Pattern | Key Developments |
Initial Reconnaissance | Feb-Mar 2025 | Sporadic testing | Infrastructure establishment, target research |
Original Campaign | Apr-May 2025 | Focused bursts | Basic Phish kits |
Operational Pause | June 2025 | Minimal activity | Likely infrastructure changes, expanded recon |
Major Escalation | Jul-Sep 2025 | Coordinated campaigns | Phish Kit rotation, Highly targeted campaigns Multi-target bursts, sustained pressure |
The repetition and timing suggest automation and possible kit-based orchestration.
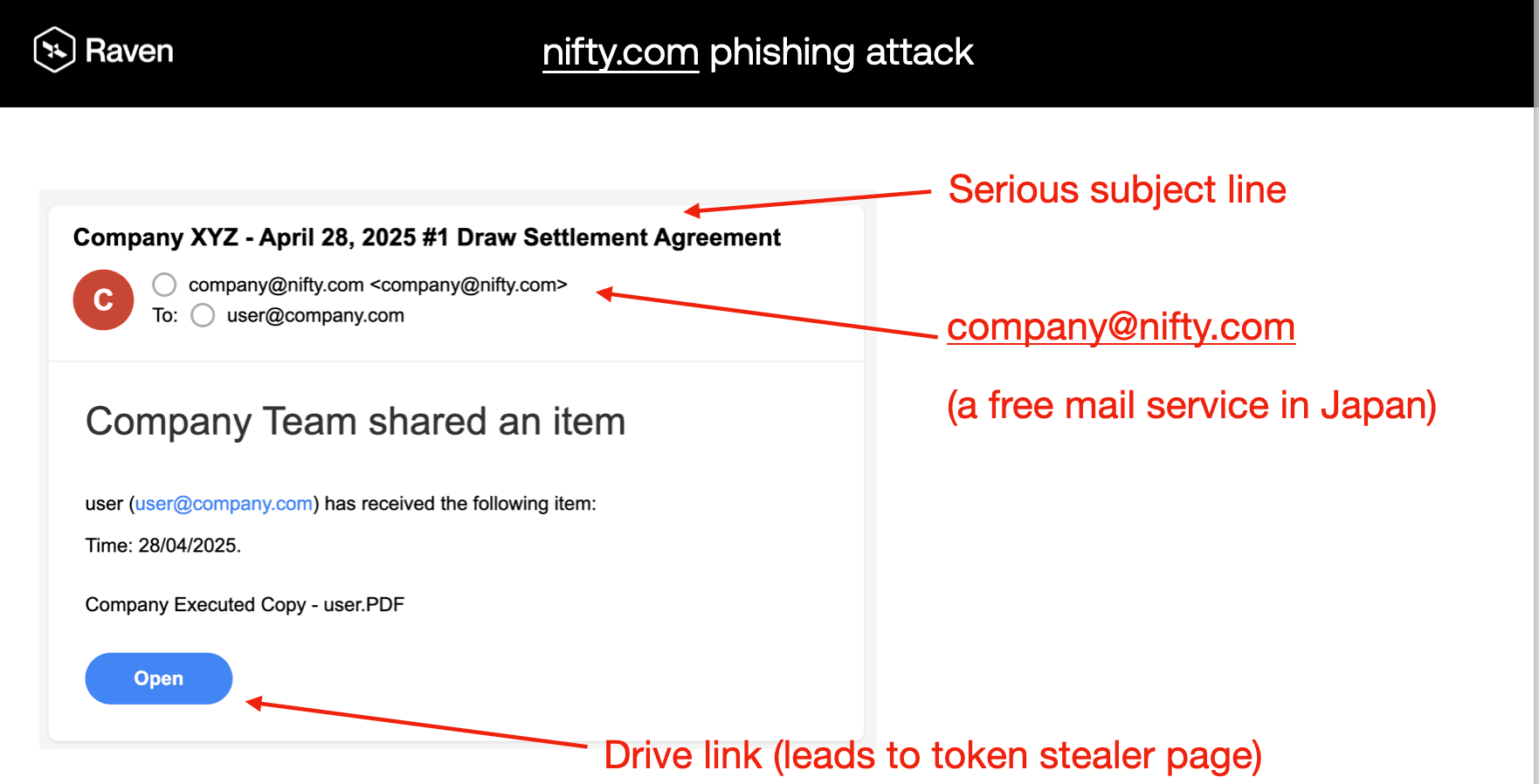
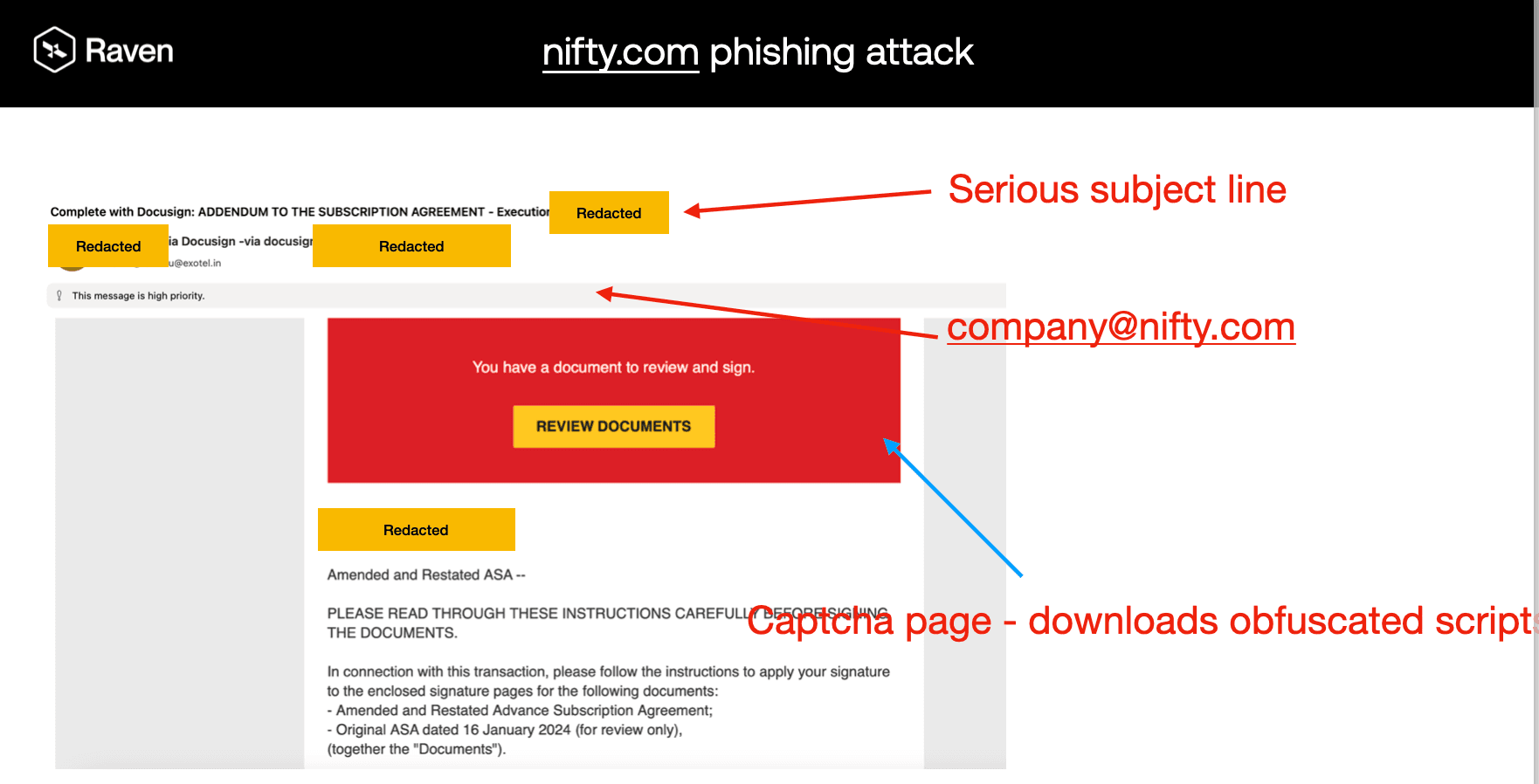
Expanded Targeting Profile: Beyond Initial Scope
New Target Categories Identified
Venture Capital Ecosystem (Primary Focus):
- Investment partners and analysts
- Portfolio company executives
- Due diligence teams
- Financial decision makers
Technology Startups:
- C-level executives (CEO, CTO, COO)
- Co-founders and technical leaders
- Business development teams
- Marketing and operations heads
Geographic and Sector Expansion
The threat actor has moved beyond the initial Japanese ISP abuse to target:
- Financial technology companies
- Software development firms
- Digital marketing agencies
- Enterprise software providers
High-Value Individual Targeting
Analysis reveals strategic focus on decision makers with financial authority:
- 75% of targets hold senior leadership positions
- Concentrated attacks on individuals with investment/financial responsibilities
- Multi-level targeting within same organizations for comprehensive intelligence gathering
Anatomy of the Campaign
1. Infrastructure Used
Domain: nifty[.]com (legitimate Japanese ISP)
Mail Servers: mta-snd-e0X.mail.nifty[.]com
IP Ranges: 106.153.226.0/24, 106.153.227.0/24
Sender Accounts: Free consumer addresses impersonating businesses
2. Payload and Delivery Method
No links in the email body
Malicious attachments:
File types: .pdf and .html
Filenames like: SAFE_Terms_May2025.pdf, Execution_Agreement.html
Redirect chain (sanitized):
clickme[.]thryv[.]com → benign-looking marketing tracker
2vf78gnafutdc5zqmhng[.]iqmwpx[.]ru → phishing site with obfuscated JavaScript
Embedded email in URL fragment for tracking (e.g., #[email protected])
3. Techniques Designed to Evade Detection
HTML padding: Use of whitespace characters (=20, ) to bypass filters
Multipart MIME structure: Payloads hidden in attachments
Display name spoofing: Examples like “Name via DocuSign” to imply legitimacy
Obfuscated links: Redirectors that aren't obvious bad URLs
Flawless grammar and tone: Indicative of AI-generated or phishing kit templates
4. Behavioural Indicators Flagged by Raven
Unusual sender-recipient combinations
Repeated use of contract-related lures across recipients
Brand impersonation in display names
Identical attachment patterns across campaigns
Obfuscated redirect chains leading to flagged infrastructure
Threat Classification
Vector: Abuse of authenticated Nifty.com mail infrastructure
Attack Type: Redirect-based phishing delivered via file attachments
Intent: Credential harvesting, including Gmail session/token theft
Sophistication Level: Medium to High — use of evasive techniques and infrastructure blending
Attribution Signals: Likely use of phishing kits, with signs of automation or AI-generated content
Attribution and Sophistication Assessment
Threat Actor Maturation
Sophistication Indicators:
- 8-month operational persistence
- Strategic target selection focused on financial decision makers
- Technical capability evolution with advanced evasion techniques
- Coordinated campaign orchestration across multiple organizations
Operational Security Evolution
Enhanced OPSEC Measures:
- Infrastructure layering (Nifty + ConvertKit + rotating domains)
- Payload obfuscation through encoding and multi-stage redirects
- Timing diversification across business and off-hours
- Geographic domain rotation for payload hosting
Campaign Scale Assessment
Resource and Capability Indicators:
- 100+ total attack instances over 8 months
- Multiple simultaneous organizational targeting
- Sustained operational tempo with burst capabilities
- Advanced social engineering with contextual business lures
Detection Layer | Original Signals | New Indicators |
Infrastructure | Nifty.com domains | + ConvertKit redirect patterns |
Content | Document lures | + Base64 URL encoding detection |
Behavioral | Sender patterns | + Burst campaign timing analysis |
Targeting | Display name spoofing | + Executive/financial role targeting |
Why Most Defenses Missed It
Legacy email security often relies on:
Broken SPF/DKIM
Blacklisted domains
Suspicious URLs in body
Behavioral triggers from mail headers
This campaign had none of those.
What Raven Recommends
Defending against this class of attack requires going beyond basic hygiene:
Recommendation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Flag unknown senders on free domains | Even if technically valid |
Sandbox all attachments | Payloads often live inside file contents |
Inspect display names & MIME structures | True impersonation often happens here |
Watch for document lures without context | Especially execution, SAFE, or stock agreements |
Don’t trust authentication blindly | SPF/DKIM passing ≠ safe content |
Conclusion: An Evolving and Persistent Threat
Our updated analysis reveals that the Nifty.com phishing campaign identified in Feb-May 2025 was not an isolated incident but the beginning of sustained operations. The threat actor has demonstrated:
- Remarkable operational persistence across 8 months
- Strategic targeting evolution focusing on financial decision makers
- Technical capability advancement with sophisticated evasion techniques
- Coordinated campaign orchestration with burst attack patterns
Organizations in the venture capital and financial technology sectors should treat this as an active, evolving threat requiring enhanced defensive measures and continuous monitoring.
The combination of legitimate infrastructure abuse, advanced social engineering, and persistent operations makes this threat actor a significant concern for the broader financial and technology investment ecosystem.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted